2021/03/02
Alterations in serum magnesium levels are presented as a new risk factor in liver disease
Liver disease patients presented altered serum magnesium levels and significantly elevated expression of the CNNM4 protein, a modulator of this cation in the liver.
Targeted regulation of CNNM4 by GalNac-siRNA technology developed by Silence Therapeutics opens a novel therapeutic window for liver disease.
The study has been published in the international Journal of Hepatology, one of the highest impact journals in its field.
(Bilbao, 2 March 2021). Individuals with alterations in magnesium levels have an increased risk of presenting fatty liver disease with inflammation and fibrosis, as concluded by a study that has just been published in Journal of Hepatology.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, characterized by inflammation and liver fibrosis, is associated with obesity and has a worldwide prevalence of 1.7 billion people.
Unhealthy nutritional habits and dietary imbalances are recognized as the main cause of many diseases. Magnesium is widely distributed in both the plant and animal food supply. Most vegetables, legumes, peas, beans and nuts are rich in magnesium, as are some seafood and spices.
In recent years, there has been growing concern about defective magnesium intake in the general population. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 79% of U.S. adults do not meet the recommended intake of this cation.
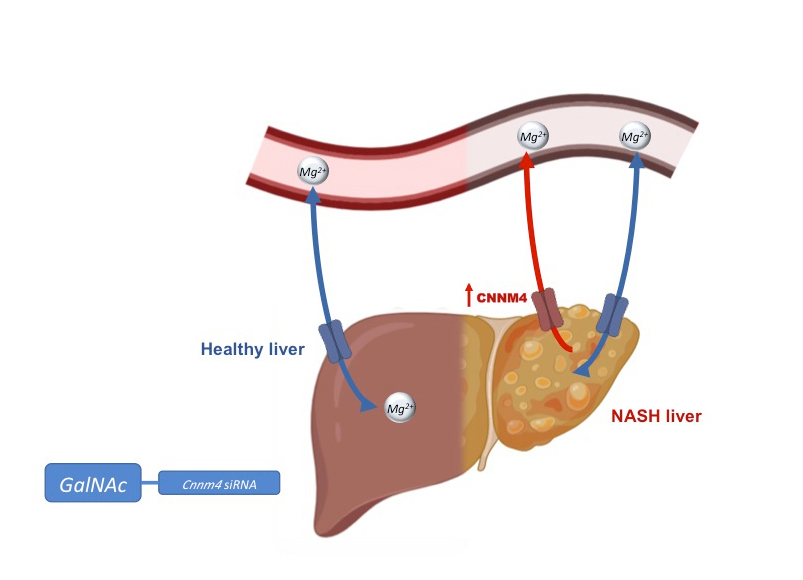
The study, led by Dr. Malu Martínez Chantar, Principal Investigator of the Liver Disease laboratory of (CIC bioGUNE -a member of the Basque Research & Technology Alliance BRTA- and CIBER de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), and Dr. Jorge Simon, first author of the publication, has shown a higher expression of the CNNM4 protein in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. CNNM4 acts as a transporter of magnesium out of the liver, being responsible for the imbalance in the levels of this cation, that ends in the development of liver disease.
"These patients have an altered magnesium export machinery that increases the vulnerability of their liver to suffer inflammatory processes, development of fibrosis and fat deposition," explains Dr. Martínez Chantar. “This study also presents a novel therapeutic approach based on GalNac-siRNA technology that specifically targets the liver by modulating CNNM4 levels. The CNNM4 molecule developed from Silence Therapeutics’ proprietary mRNAi GOLD™ (GalNAc Oligonucleotide Discovery) Platform effectively protects from liver pathology in preclinical models of steatohepatitis.”
This molecule opens an unexplored therapeutic window in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
“The study underscores the importance of magnesium balance for supporting liver health. With insight into how this essential metal affects lipid metabolism at the cellular level, possible therapeutic targets for this and other liver pathologies start emerging,” says Daniela Buccella, associate professor of chemistry at New York University and a study co-author.
This work, carried out in collaboration with Dr. Alfonso Martinez de la Cruz from CIC bioGUNE, Drs. Patricia Aspichueta and Cesar Martin from the University of the Basque Country, Dr. Daniela Buccella from New York University, Dr. Javier Crespo, researcher at the University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla/IDIVAL, Dr. Guadalupe Sabio Fundación Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III, Dr. Franz Martin from CABIMER, Universidad Pablo de Olavide, CIBERDEM, Dr. Ute Schaeper of Silence Therapeutics and a consortium of national researchers, has been published in the international Journal of Hepatology, one of the highest impact journals in its field.
The full publication can be found here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168827821000945
About CIC bioGUNE
The bioGUNE Research Center, a member of the Basque Research & Technology Alliance (BRTA), based at the Bizkaia Science and Technology Park, is a biomedical research organization that develops cutting-edge research at the interface between structural, molecular and cellular biology, with a special focus on the study of the molecular basis of disease, to be used in the development of new diagnostic methods and advanced therapies. CIC bioGUNE is recognized as a "Severo Ochoa Center of Excellence", the highest recognition of centers of excellence in Spain.
About BRTA
The BRTA is an alliance made up of 4 collaborative research centres (CIC bioGUNE, CIC nanoGUNE, CIC biomaGUNE and CIC energiGUNE) and 12 technology centres (Azterlan, Azti, Ceit, Cidetec, Gaiker, Ideko, Ikerlan, Lortek, Neiker, Tecnalia, Tekniker and Vicometch), with the aim of developing advanced technological solutions for Basque companies.
With the support of the Basque Government, the SPRI Group and the Provincial Councils of the three regional provinces, the alliance seeks to promote collaboration among its centres, to strengthen the conditions to generate and transfer knowledge to companies, contributing to their competitiveness, and to spread Basque scientific and technological capacity.
BRTA has a staff of 3,500 professionals, accounts for 22% of the Basque Country’s R&D investment, generates an annual turnover of over EUR 300 million and files 100 European and international patents per year.
CIC bioGUNE, member of the Basque Research & Technology Alliance - BRTA
CIBER (Consorcio Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red, M.P.) depends on the Instituto de Salud Carlos III -Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades- and is co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
About CABIMER
CABIMER (Centro Andaluz de Biología Molecular y Medicina Regenerativa – Andalusian Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medicine Centre) is a groundbreaking multidisciplinary biomedical research centre in Andalusia, drawing together basic and applied research with the aim of transforming the results of the scientific work carried out there into direct improvements to citizens’ health and quality of life.
About Instituto de Investigación Marqués de Valdecilla (IDIVAL)
IDIVAL is the Sanitary Research Institute of Cantabria, accredited by the Spanish Institute of Health Carlos III, that promotes and develops innovation and health research in the biosanitary environment of the region. IDIVAL has 31 health research groups in the areas of Cancer, Neurosciences, Transplantation, Infection and immunity, Metabolism and Transversal area. In the last 5 years, IDIVAL has managed 35 million from external funding obtained by the researchers themselves through competitive projects, agreements and donations. Currently, IDIVAL is promoting research in the field of clinical trials with the participation of especially active groups such as the one led by Dr. Javier Crespo.
See a large version of the first picture