2015/01/22
Structure and interactions of a multifunctional domain of HuR protein
The human antigen R (HuR) is a powerful regulator of cancer. By binding and stabilizing certain messenger RNA molecules, it promotes the production of other proteins related to cell proliferation, survival, angiogenesis and metastasis, and therefore is a potential pharmacological target. HuR consists of three domains, and the C-terminal domain is involved in both RNA recognition and in HuR oligomerization. The structure of the C-terminal domain of HuR and its interactions has been studied by researchers at the CIC Cartuja, in Seville, and at CIC bioGUNE, mainly using NMR and molecular dynamics simulations. The three dimensional structure of the domain is characteristic of RNA binding proteins, but the regions responsible for the two different molecular recognition events (RNA binding and HuR oligomerization) are located on opposite protein faces.
This study rationalizes the multifunctional nature of the C-terminal domain of HuR and paves the way for modulating its role in cancer progression by disrupting each of the two different molecular interactions.
Link to the published article: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25584704
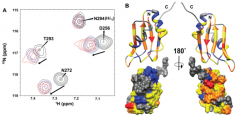
Figure. (A) Overlay of selected regions of the NMR spectra of the C-terminal domain of HuR in the presence of increasing concentrations of RNA (from black to red colors). (B) The binding interface is mapped on the threedimensional structure of the domain. The regions colored orange are those most directly involved in RNA binding.
See a large version of the first picture