2016/05/16
Our scientists develop a novel fragment-based combinatorial Nuclear Magnetic Resonance strategy for the optimization of aminoglycosides as DNA/RNA ligands
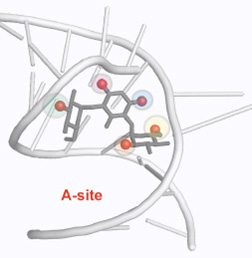
One of the most expensive and time-consuming tasks in the drug discovery process aims at developing selective binders from promiscuous lead compounds. A team of scientists from CSIC (IQOG, IQFR, and CIB), the Universities of La Rioja and Zaragoza and CIC bioGUNE have developed a novel fragment-based combinatorial Nuclear Magnetic Resonance strategy for the optimization of aminoglycosides as DNA/RNA ligands. Contrary to the common view of NMR as a low throughput technique, the reported NMR methodology represents a robust alternative for the detection of selective binders to the ribosomal decoding A-Site sequence.
For more information, see: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.6b00328
See a large version of the first picture