2023/01/30
Impaired Function of Solute Carrier Family 19 Leads to Low Folate Levels and Lipid Droplet Accumulation in Hepatocytes
Ainara Cano 1,2,†, Mercedes Vazquez-Chantada 2,3,†,‡, Javier Conde-Vancells 3, Aintzane Gonzalez-Lahera 4,5, David Mosen-Ansorena 4, Francisco J. Blanco 4,6,§, Karine Clément 7,8,9, Judith Aron-Wisnewsky 7,8,9, Albert Tran 10, Philippe Gual 10, Carmelo García-Monzón 5,11, Joan Caballería 5,12, Azucena Castro 2,‖, María Luz Martínez-Chantar 4,5, José M. Mato 4,5, Huiping Zhu 3,¶, Richard H. Finnell 3,**,†† and Ana M. Aransay 4,5,*,**
Biomedicines 2023, 11(2), 337; https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020337
Received: 30 November 2022/Revised: 17 January 2023/Accepted: 18 January 2023/Published: 25 January 2023
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metabolic and Genetic Associated Fatty Liver Diseases)
Abstract
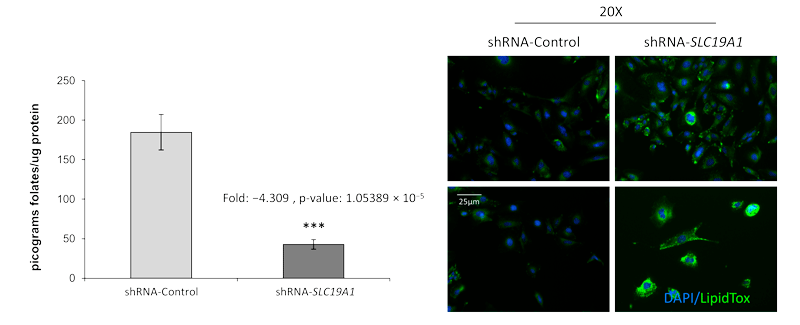
Low serum folate levels are inversely related with metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). The role of the folate transporter gene (SLC19A1) was assessed to clarify its involvement in lipid accumulation during the onset of MAFLD in humans and in liver cells by genomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic techniques. Genotypes of 3 SNPs in a case-control cohort were initially correlated to clinical and serum MAFLD markers. Subsequently, the expression of 84 key genes in response to the loss of SLC19A1 were evaluated with the aid of an RT2profiler-array. After shRNA-silencing of SLC19A1 in THLE2-cells, folate and lipid levels were measured by ELISA and staining techniques, respectively. In addition, up to 482 amino acids and lipid metabolites were semi-quantified in SLC19A1-knockdown (KD) cells through ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. SNPs, rs1051266 and rs3788200, were significantly associated with the development of fatty liver for the single-marker allelic test. The minor alleles of these SNPs were associated with a 0.6/-1.67-fold decreased risk of developing MAFLD. When SLC19A1 was KD in THLE2 cells, intracellular folate content was four-times lower than in wild-type cells. The lack of functional SLC19A1 provoked significant changes in the regulation of genes associated with lipid droplet accumulation within the cell and the onset of NAFLD. Metabolomic analyses showed a highly altered profile, where most of the species that became accumulated in SLC19A1-KD-cells belong to the chemical groups of triacylglycerols, diacylglycerols, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and long chain, highly unsaturated cholesterol esters. In conclusion, the lack of SLC19A1 gene expression in hepatocytes affects the regulation of key genes for normal liver function, reduces intracellular folate levels, and impairs lipid metabolism, which entails lipid droplet accumulation in hepatocytes.
Leyenda de las direcciones de las instituciones colaboradoras
1 Food Research, AZTI, Basque Research and Technology Alliance (BRTA), Parque Tecnologico de Bizkaia, Astondo Bidea, Building 609, 48160 Derio, Spain
2 OWL Metabolomics, Parque Tecnologico de Bizkaia, Building 502, 48160 Derio, Spain
3 Department of Nutritional Sciences, Dell Paediatric Research Institute, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712, USA
4 CIC bioGUNE, Parque Tecnologico de Bizkaia, Building 801-A, 48160 Derio, Spain
5 CIBERehd, ISCIII, 28029 Madrid, Spain
6 Ikerbasque, Basque Foundation for Science, 48009 Bilbao, Spain
7 Nutriomics Research Group, Nutrition Department, Pitié-Salpétrière Hospital, INSERM, Sorbonne Université, F-75013 Paris, France
8 INSERM, UMR_S 1166, NutriOmics Team 6, F-75013 Paris, France
9 Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris, Nutrition Department ICAN and CRNH-Ile de France, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, F-75013 Paris, France
10 Team 8 “Chronic Liver Diseases Associated with Obesity and Alcohol”, INSERM, U1065, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice, C3M, Université Côte d’Azur, 06000 Nice, France
11 Liver Research Unit, Santa Cristina University Hospital, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa, 28009 Madrid, Spain
12 Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic, 08036 Barcelona, Spain
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
‡ Current Address: Mercedes, MBP, Discovery Sciences, IMED Biotech Unit AstraZeneca, Cambridge CB4 0WG, UK.
§ Current Address: Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas Margarita Salas (CIB), CSIC, 28040 Madrid, Spain.
‖ Current Address: Basque Trade & Investment/Agencia Vasca de Internacionalización, 48011 Bilbao, Spain.
¶ Current Address: Nuclein, LLC., Austin, TX 78710, USA.
** Co-Senior Authors.
†† Current Address: Center for Precision Environmental Health Departments of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Molecular and Human Genetics, and Medicine, Office: Alkek Tower Rm. N1317.09. Baylor College of Medicine, One Baylor Plaza, BCM229, Houston, TX 77030, USA.
See a large version of the first picture